
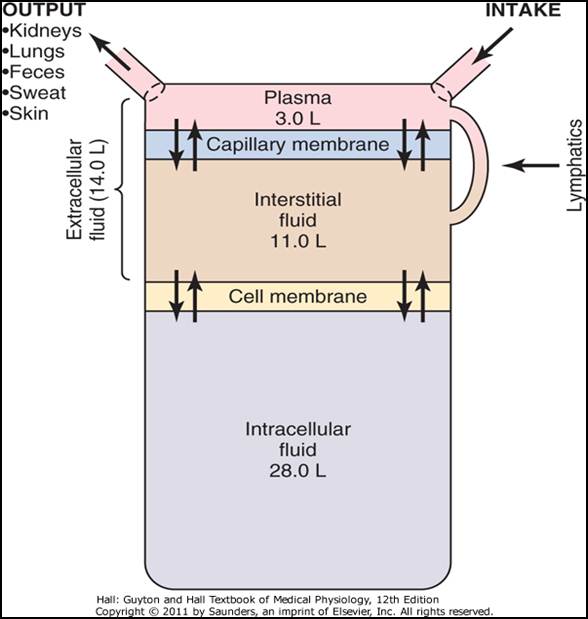
An electrolyte is a compound that separates into ions (charged particles) when it dissolves in water. (From Hall JE: Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology, ed 12, Philadelphia, 2011, Saunders.)įluid in the body compartments contains mineral salts known technically as electrolytes. Transcellular fluids such as cerebrospinal, pleural, peritoneal, and synovial fluids are secreted by epithelial cells ( Hall, 2011).įIG. Interstitial fluid is located between the cells and outside the blood vessels. Intravascular fluid is the liquid portion of the blood (i.e., the plasma). ECF has two major divisions (intravascular fluid and interstitial fluid) and a minor division (transcellular fluids). ECF is approximately one third of total body water. In adults ICF is approximately two thirds of total body water. The term fluid means water that contains dissolved or suspended substances such as glucose, mineral salts, and proteins.īody fluids are located in two distinct compartments: extracellular fluid (ECF) outside the cells, and intracellular fluid (ICF) inside the cells ( Fig. Obese people have less water in their bodies than lean people because fat contains less water than muscle. Women typically have less water content than men. This proportion decreases with age approximately 50% of an older man’s weight is water. In fact, about 60% of the body weight of an adult man is water. Water makes up a substantial proportion of body weight. Location and Movement of Water and Electrolytes This section provides the foundation for your critical thinking regarding patients who have or are at risk of having, fluid, electrolyte, or acid-base imbalances. You also learn how imbalances develop how various fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base imbalances affect patients and ways to help patients maintain or restore balance safely. In this chapter you learn how the body normally maintains fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance. All of these characteristics have regulatory mechanisms, which keeps them in balance for normal function. These characteristics include the fluid amount (volume), concentration (osmolality), composition (electrolyte concentration), and degree of acidity (pH). The characteristics of body fluids influence body system function because of their effects on cell function. Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balances within the body maintain the health and function of all body systems. Body fluids contain electrolytes such as sodium and potassium they also have a certain degree of acidity.
Iv fluids and body fluid compartments how to#
Explain how to change intravenous solutions and tubing and discontinue an infusion.

Describe how to measure and record fluid intake and output.

Describe the processes involved in regulating plasma concentrations of potassium, calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions.Describe the processes involved in regulating extracellular fluid volume, body fluid osmolality, and fluid distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
